
These cations are present in haemoglobin which is an integral part of red blood cells, necessary for human life. You can find iron cations in many of the foods we eat such as seafood and beans. Lastly, iron cations are a vital part of human survival. It is a malleable, ferromagnetic, ductile. The melting point of a substance is the temperature at which this phase change occurs. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word ferrum meaning iron. In general, melting is a phase change of a substance from the solid to the liquid phase. Note that, these points are associated with the standard atmospheric pressure. Iron ores are rocks (brown-red colour) from which elemental iron is extracted. Iron Melting Point Melting point of Iron is 1538☌. Iron is found in its native state in meteorites, the core of the Earth and the core of dying stars.
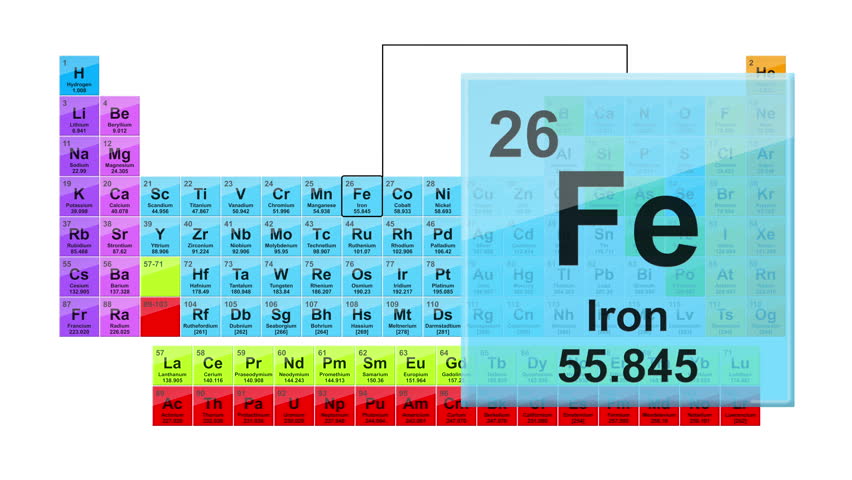
Iron’s colour is silvery grey as shown in the background. Periodic Table: Alchemy Iron Iron is one of the seven metals of alchemy (gold, silver, mercury, copper, lead, iron & tin). To make the F, an Egyptian vase and eating utensils were used because the first evidence of the use of iron dates back over 5,000 years ago when Egyptians used it to make tools and weapons during the “Middle Bronze Age and Iron Age”. Iron is notable for being the final element produced by stellar nucleosynthesis, and thus the heaviest element which does not require a supernova or similarly cataclysmic event for its formation. Iron: Iron has been used throughout ancient times and it is found in different places throughout the universe. Iron is a chemical element in the periodic table that has the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. The Fe-54 isotope is used for the production of radioactive Fe-55 which in. Studies have included iron-loss by human adolescents, conditions for effective iron absorption, interventions for anemia and genetic iron control. Pyykkö, personal communication, 1998, 204, 2008, 2010.PREVIOUS | NEXT York Memorial Collegiate Institute, Toronto, Ontario Canada Iron isotopes are mainly used in nutritional studies, with Fe-57 and Fe-58 being the two most commonly used Fe isotopes. Lide, (ed.), CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics 1999-2000 : A Ready-Reference Book of Chemical and Physical Data (CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, USA, 79th edition, 1998. I am grateful to Professor Pekka Pyykkö (University of Helsinki, Finland) who provided the nuclear quadrupole moment data in this and the following two references. Where given, data for certain radioactive nuclei are from this reference. Iron (Fe) is a chemical element of the periodic table, located in the group 8 and the period 4, and is having the atomic number 26. Mason in Multinuclear NMR, Plenum Press, New York, USA, 1987. (Buy two and they could make great but large earrings. I am grateful to Professor Robin Harris (University of Durham, UK) who provided much of the NMR data, which are copyright 1996 IUPAC, adapted from his contribution contained within this reference. The element of Iron on The Periodic Table of Elements, in the form of a fashionable pendant/necklace. It is the cheapest metal and is the fourth most abundant element on earth. It is a ductile, lustrous, silvery-grey transition metal, whose name comes from the Anglo-Saxon word iren.

5, John Wiley & Sons, Chichester, UK, 1996. Iron (Fe) is a chemical element of the periodic table, located in the group 8 and the period 4, and is having the atomic number 26. Harris in Encyclopedia of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, D.M.

Magnetogyric ratio, γ (10 7 rad T ‑1 s -1) Table of NMR-active nucleus propeties of iron Ĭommon reference compound: Fe(CO) 5/C 6D 6. Kuchitsu in Quantities, Units and Symbols in Physical Chemistry, Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, UK, 1988. According to this question, the periodic table reveals that iron (Fe) has an atomic mass of 56 amu, oxygen (O) has an atomic mass of 16 amu, and hydrogen (H) has a mass of 1 amu.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
